Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
MRIUltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events

- Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
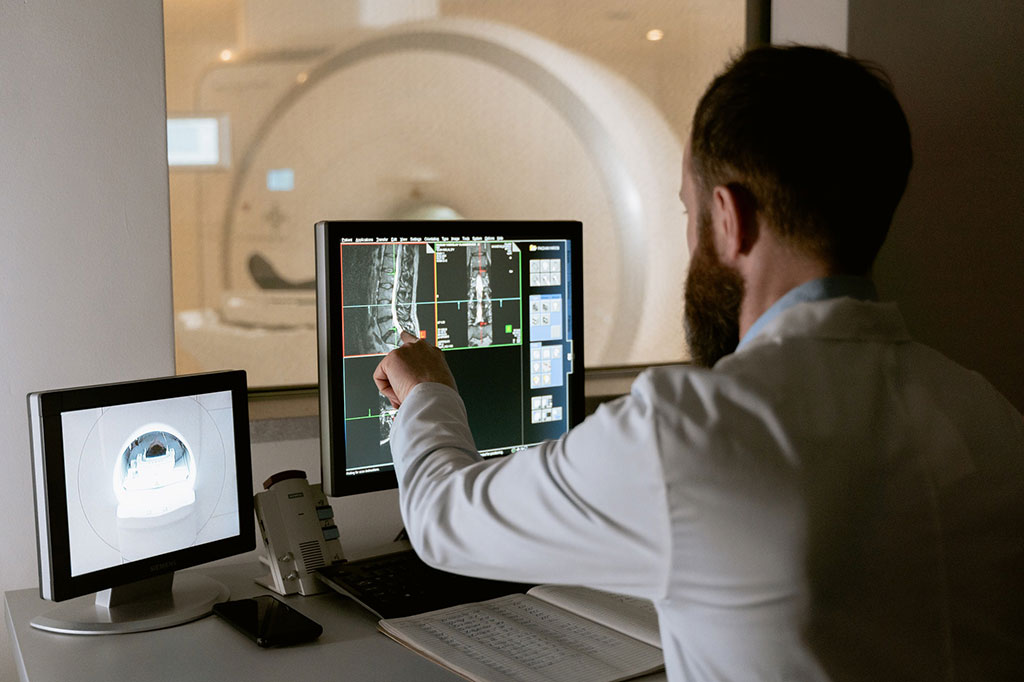
- AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
- MRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
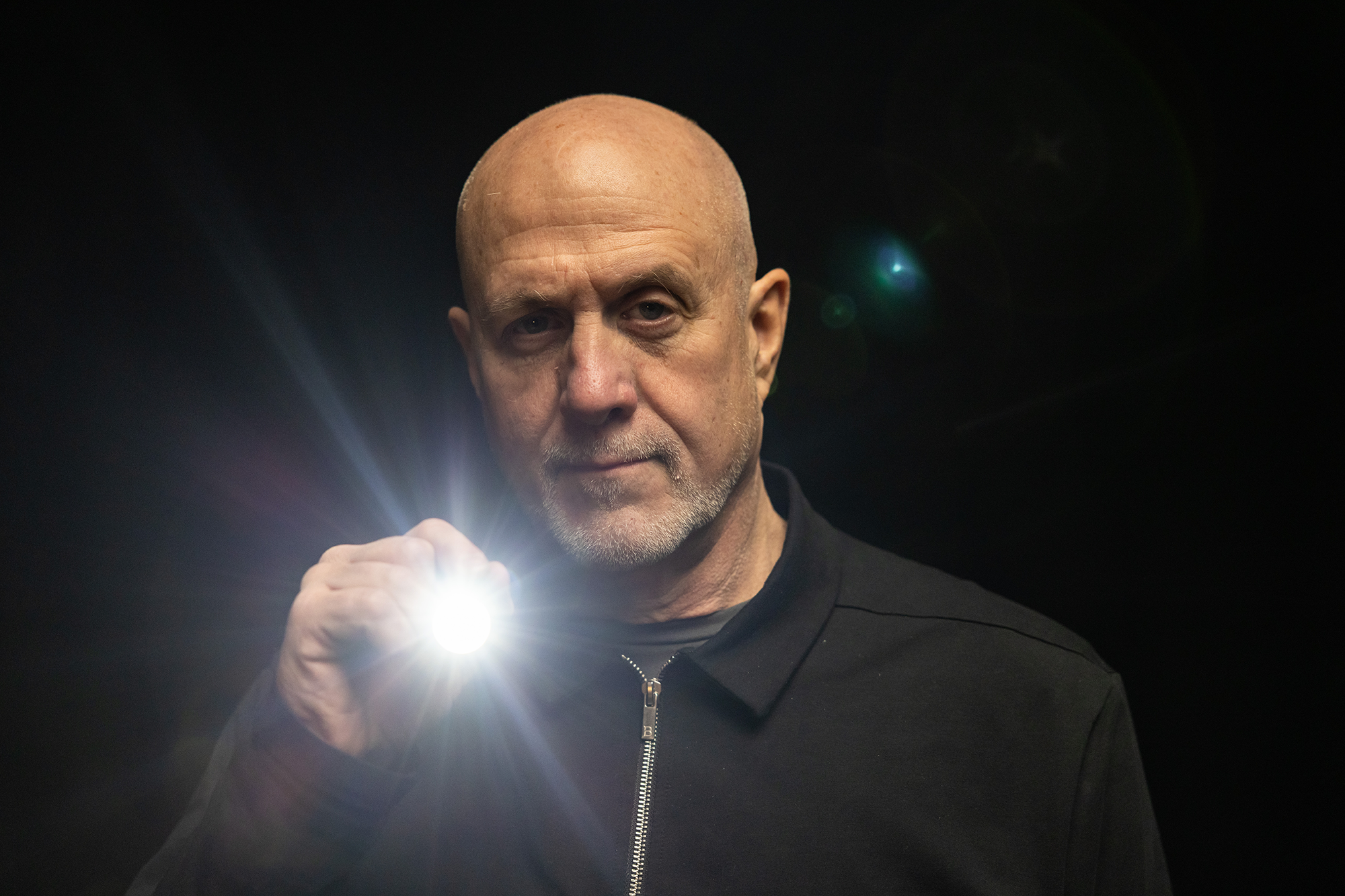
- Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
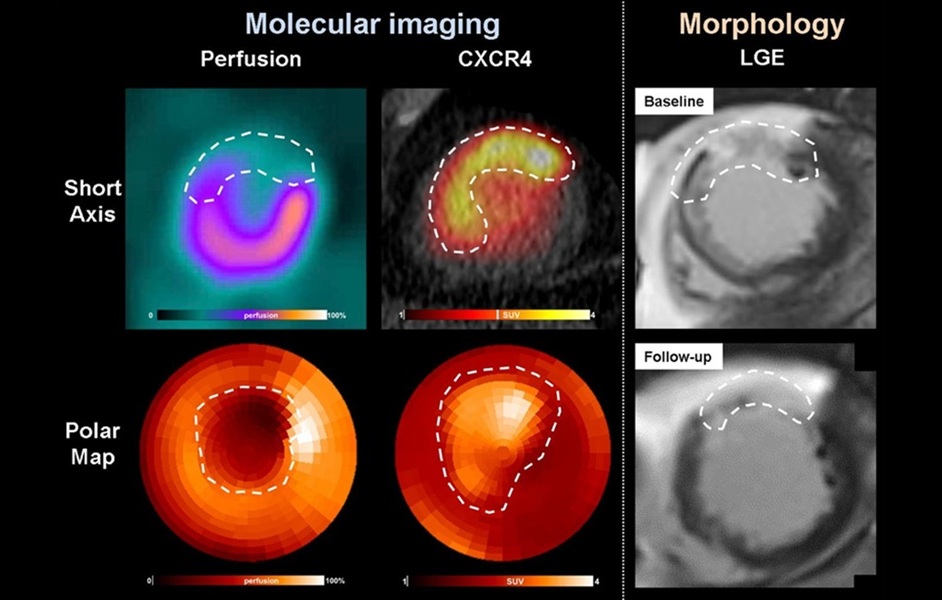
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
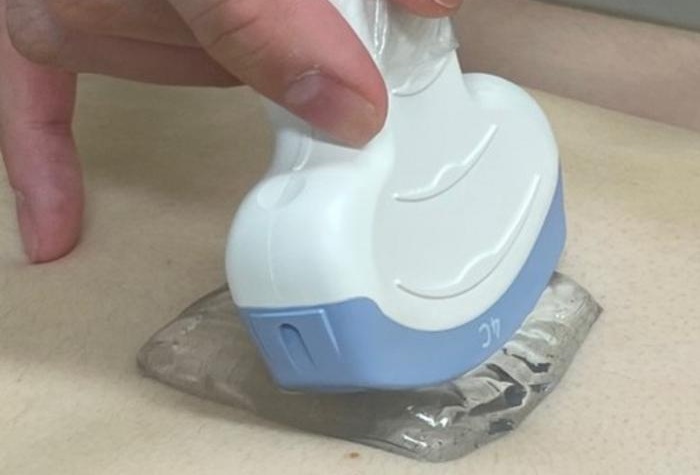
- Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
- AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
- Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
- Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
- Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
- AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
- New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
- AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
- AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
- New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
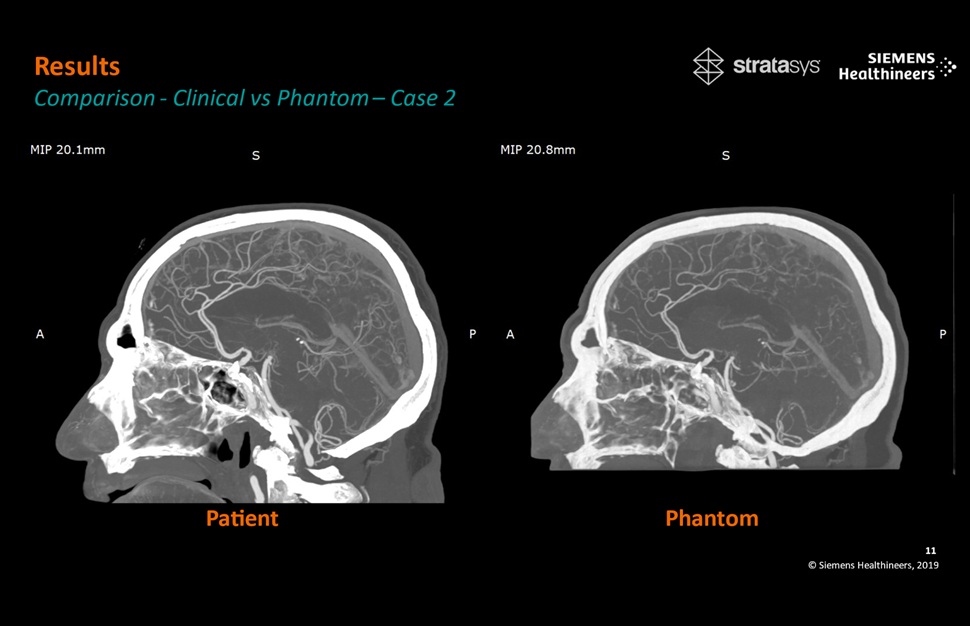
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery

 Expo
Expo
- Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
- MRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
- Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
- AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
- Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
- Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
- Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
- AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
- New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
- AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
- AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
- New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery