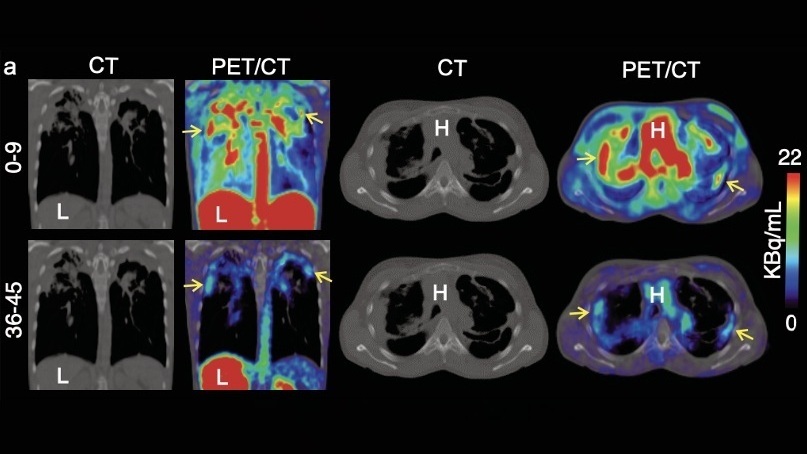
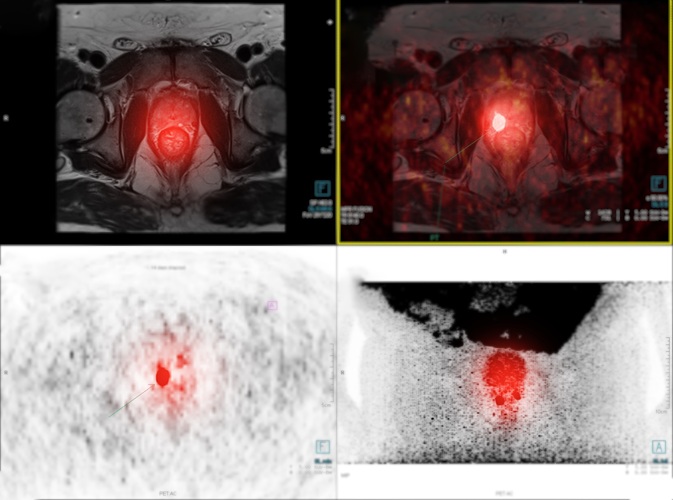
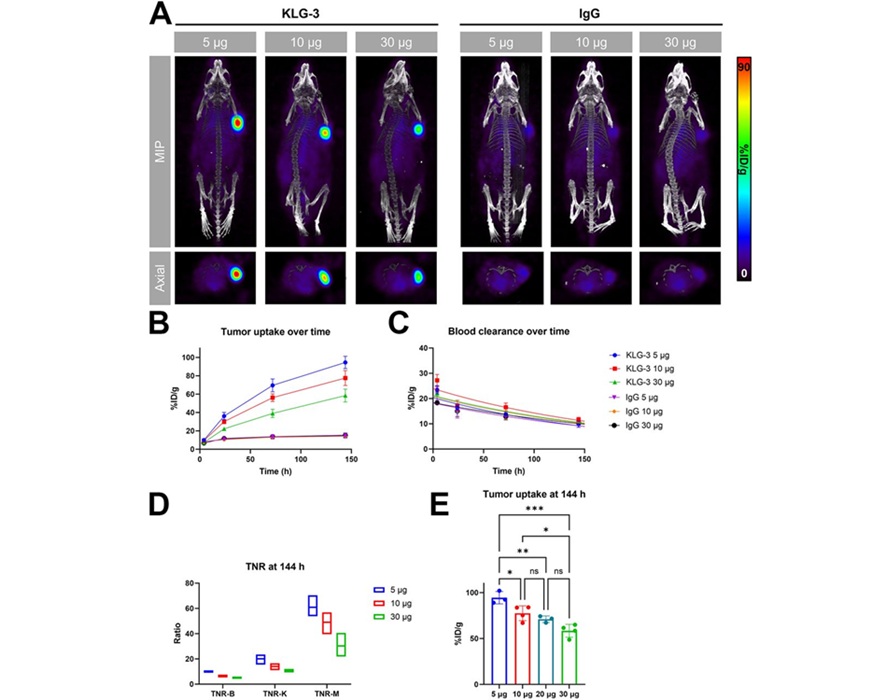
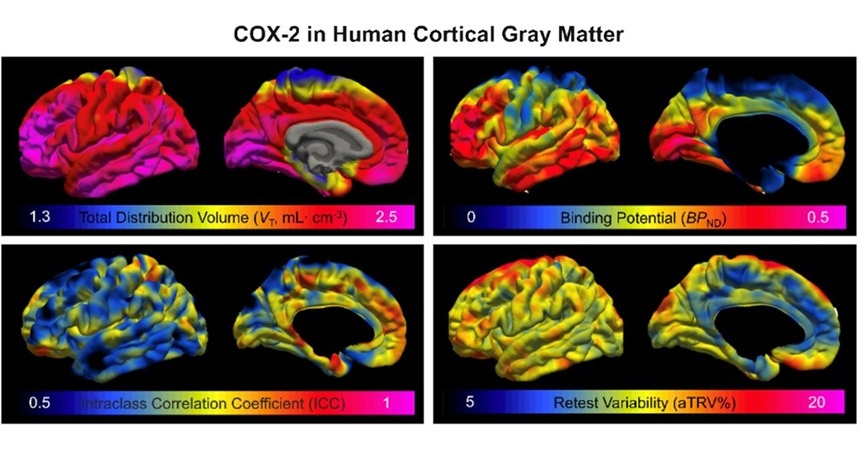
Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Radiography
UltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging ITIndustry News
Events

- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
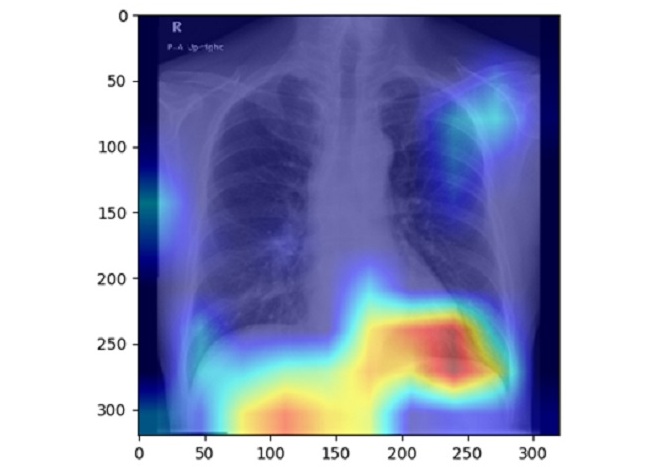
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds
- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
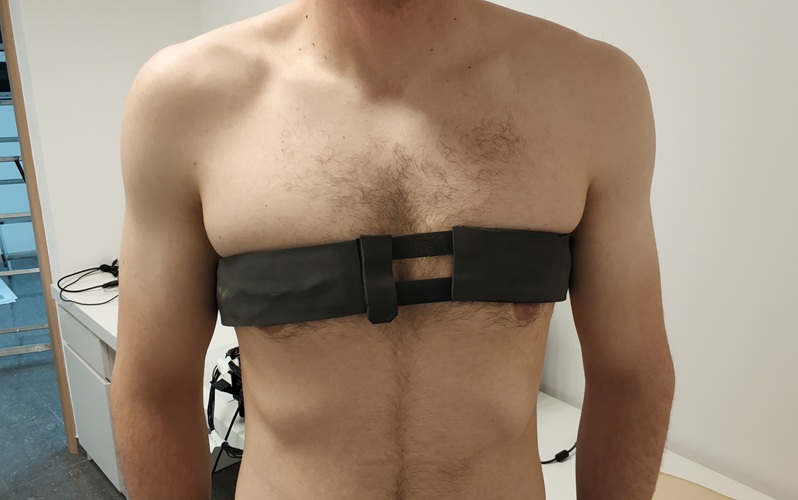
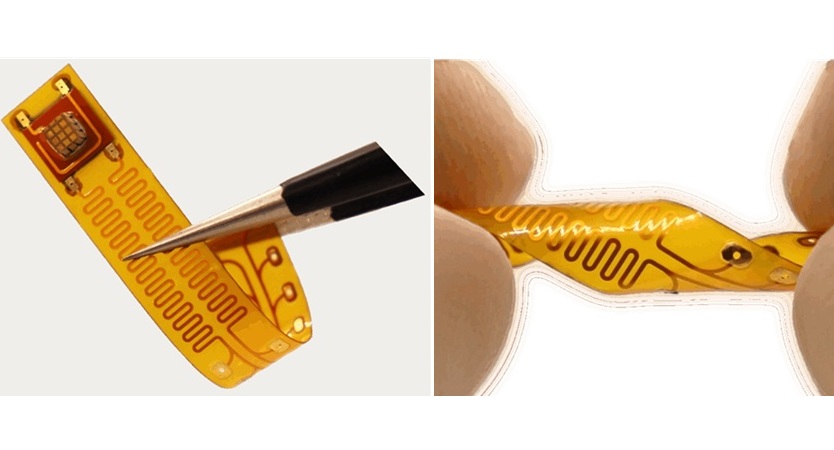
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
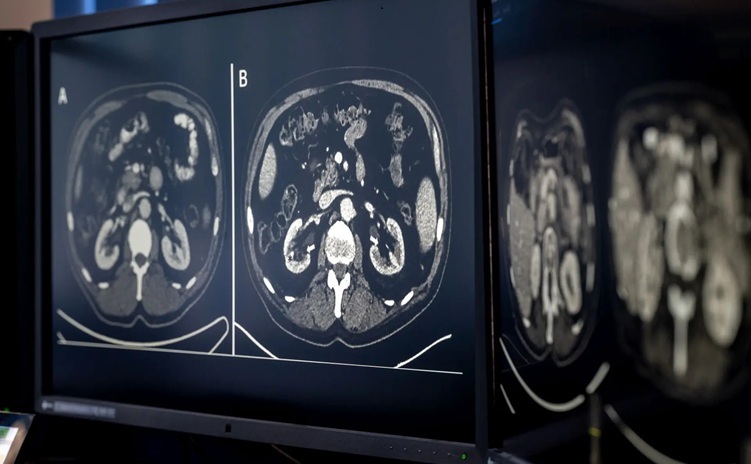
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
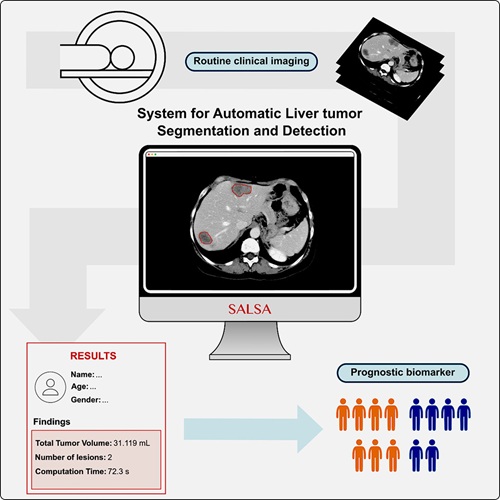
- CT-Based Deep Learning-Driven Tool to Enhance Liver Cancer Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
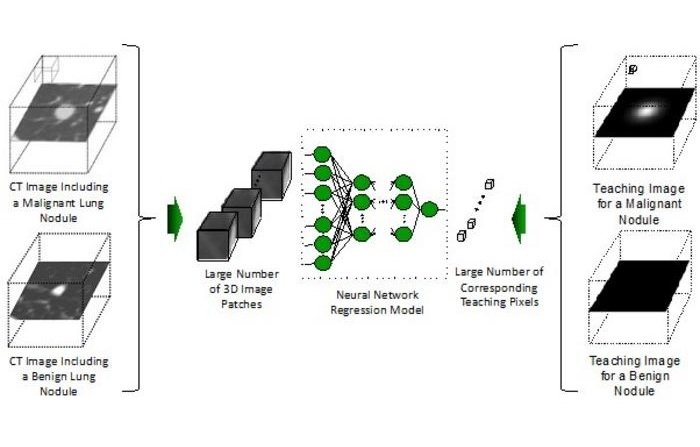
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
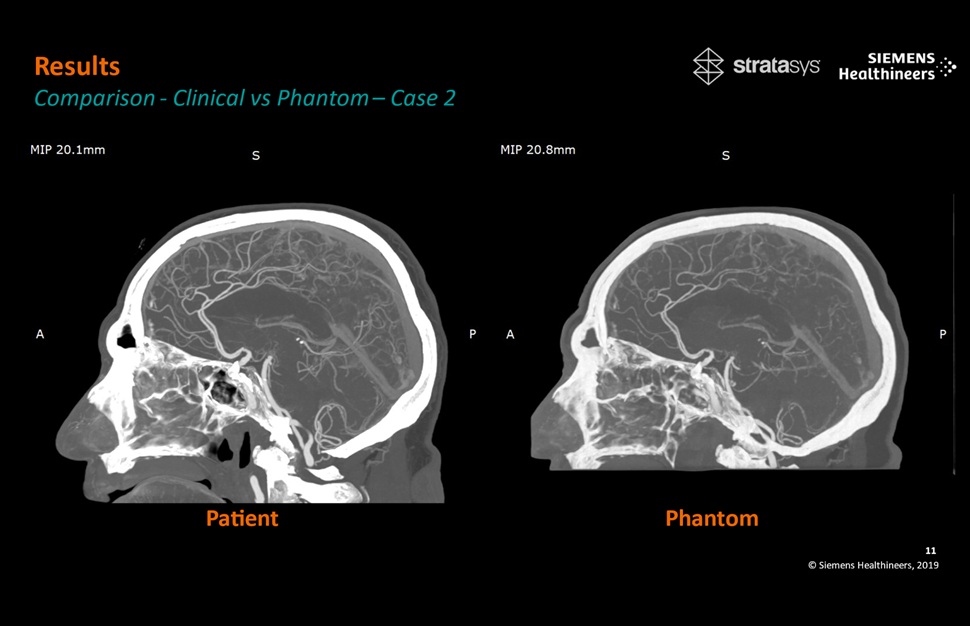
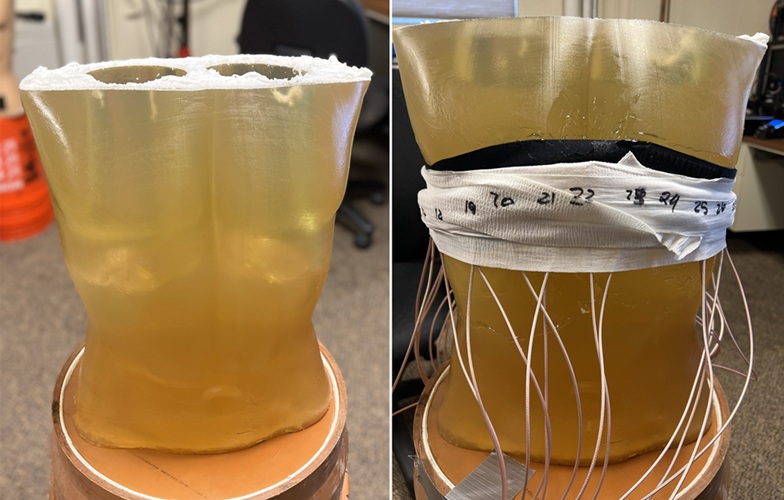
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
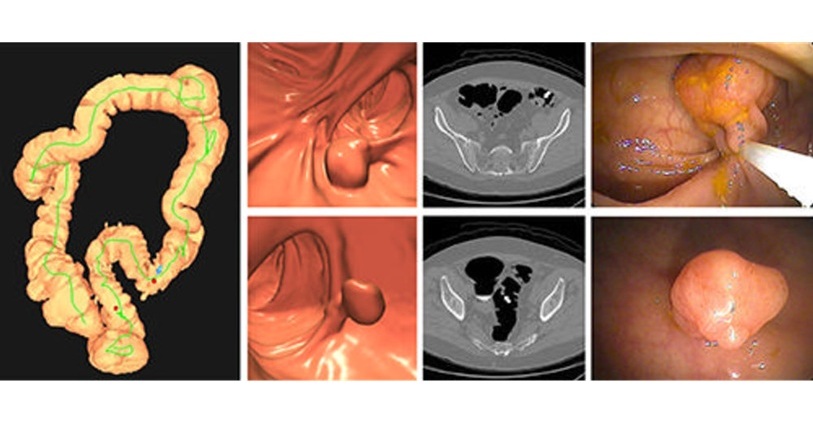
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care

 Expo
Expo
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds
- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
- CT-Based Deep Learning-Driven Tool to Enhance Liver Cancer Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care




















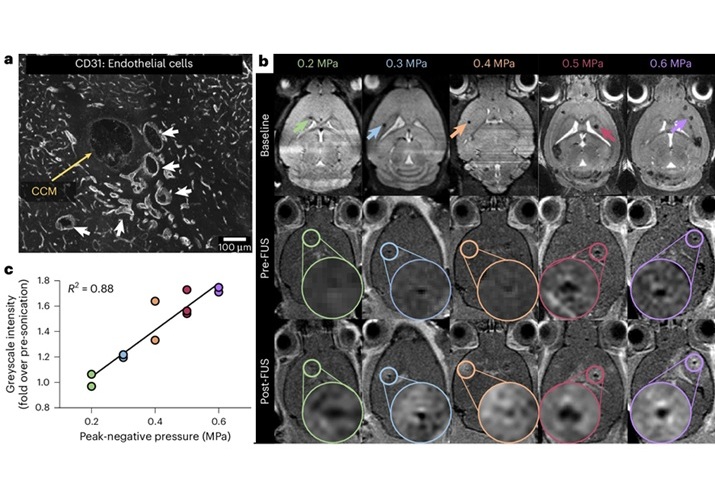
.jpeg)